
We all from time to time to make wrong decisions, but did you know whatmental obstacles can knock you out of the way?
There are a number of cognitive distortions that affect our behavior, from what we eat, and ending with the promotion of the career ladder, and keep us in the implementation of our plans.
Below are the 20 most common cognitive distortions that can prevent you from making the right choice.
Cognitive biases
The effect of the armature

People rely too much on the first information they hear. The negotiations concerning wages, the one who makes the first offer. establishes reasonable prospects according to the person.
Availability heuristic

People exaggerate the importance of the information available to them. A person can argue that smoking is not harmful, because he knows someone dozhivshego to 100 years, who smoked three packs of cigarettes a day.
The effect of herd

The likelihood that people will take the belief increases based on the number of people who are adherents of this view.
This powerful form of groupthink is one of the reasons why the meeting are often counterproductive.
The blind spot on cognitive distortions

Failure to recognize their own errors of thought, too, is a distortion. People tend to ignore the cognitive and motivational distortions in others much more often than at home.
The distortion in the perception of their own choice

When you select something, you tend to feel positive emotions, even if this option has flaws. For example, you think your dog the best, even if she occasionally biting other people.
Clustering Illusion

This trend is seen in the scheme of random events. It helps to understand the different errors in gambling, such as the belief that the likely fall on the roulette red cell after a series of red.
Confirmation Bias
We tend to listen only to the information that confirms our prejudices.
Errors thinking
Distortion of conservatism

This is where people prefer the previous evidence, not new evidence and information that appeared. People do not just accept the fact that the Earth is round, as they had the first glimpse of what it is flat.
Error classification

The tendency to look for information when it does not affect the action. More information - it is not always good. With less information people often make more accurate predictions.
Ostrich Effect
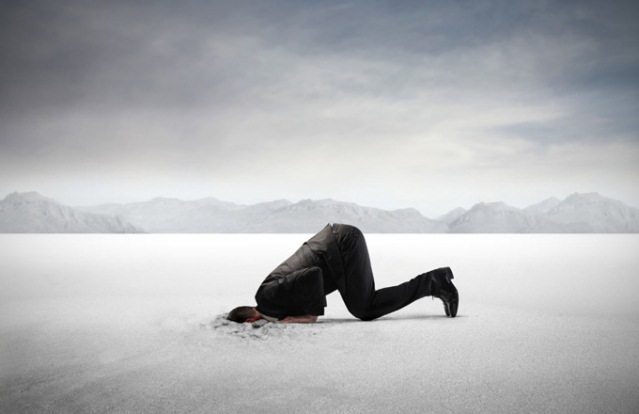

The decision to ignore the danger or negative information, burying his head in the sand like an ostrich.
The deviation in the direction of the result

The tendency to judge the decision based on the result, and not on how it makes decisions in the moment. Winning in gambling does not mean that the decision to gamble was reasonable.
The effect of overconfidence

The tendency to overestimate their abilities, which leads to unnecessary risk in everyday life. Experts are more prone to this bias than non-professionals, as they are convinced they are right.
Placebo effect
When a simple belief in a certain effect leads to the fact that this effect is carried out. In medicine, the people who were given "dummy" often have the same physiological effect that those who took these drugs.
The bias in favor of innovation

As a supporter of innovation tend to overestimate the benefits and underestimate limitations.
Thinking Traps
The novelty effect

The tendency to attach greater importance to the latest information, rather than the old.
Relevance

The tendency to focus on easily recognizable characteristics of a person or idea. When you think about death, you are more concerned about the prospect of being killed by a lion than the probability of dying from a statistically more probable cause, such as in a car accident.
Selective perception

The trend, in which we let the expectations affect perception of the world. For instance in the game of football, one team will assume that the enemy is doing more violations.
Stereotyping

Waiting on the group or individual specific characteristics, without having the true information about the person. This allows us to quickly identify strangers as friends or enemies, but people often abuse it.
Survivorship bias

Error in which focus only on examples of survival, causing us to underestimate the situation. For example, we think that to start a business is easy, since we have not heard of those who have experienced failure.
Preference zero risk

Sociologists have found that we love certainty - even if it is ineffective. Completely eliminating the risk at the same time means that the chances of damage are reduced to zero. An example could be a situation where the person fears surgical complications more than death, despite the fact that the statistics indicate otherwise.
No comments:
Post a Comment